
Self Employment Tax Guide
Self Employment Tax Guide
Running a business and paying tax
Self Employment Tax Guide – Being self-employed means:
- Running your own business
- Being responsible to work out and pay your tax
- Dealing with HM Revenue and Customs
I have been self-employed for around 8 years now and I know when I first started with my Etsy business @gembobs_crafts I didn’t have a clue what to do with Tax & I found HMRC scary! I thought I would help you learn a few of the basics to get started…

Side hustle tax basics
What is self-employment & a self-assessment tax return? If you earn over £1,000 through side hustles, you will need to register with HMRC as self-employed.
You have a £1,000 ‘trading allowance’ – so if you earn under this, you don’t need to report or register with HMRC. When you are self-employed, you need to manage taxes yourself and you do this through your tax return (Self Assessment).

What do you need to keep track of?
Earnings – HMRC will want to know how much money you have made from your side hustles Expenses – if you had expenses over £1,000 – you need to report this to HMRC.
The more expenses you have, the lower your profits (and lower your tax bill). It’s good to keep invoices and receipts, however, if you have a bank transaction that shows the expense then that’s fine too.
What are payments on account?
Payments on account are pre-payments for the next tax year. Generally, they are half your tax liability. So if you owed HMRC £1,000 – you would also make payments on account of £500 in Jan and in July.
The first year can often sting, as you pay your liability and make an extra payment on account for the future. Don’t worry though – they come off the next tax year’s bill.
Important tax dates
The UK Tax Year runs from 06 April 2022 to 05 April 2023 If you earn over £1,000 in your side hustle/self-employment, you need to register with HMRC by 05 October following the tax year-end.
You need to file and pay any liability to HMRC by 31 January following the tax year – it’s best to file early – and you can still pay by 31 Jan.

Payments on account are due on 31 January and 31 July following the tax year
When it comes to side hustles, you are taxed on profits.
Profit = Earnings – Expenses
Therefore, tracking and claiming back on what you are allowed to, is important to lower the tax bill! You also have a £1,000 trading allowance – which you can use if your expenses are lower than £1,000.
You don’t need any receipts for this. Let’s get into what you can expense.
Self Employment Tax Guide – General Expenses
Anything you purchase ‘wholly and exclusively’ can be expensed on your tax return. So it varies depending on your industry and side hustle.
The common ones include:
If you use part of your home as an office, there are two methods you can use to calculate and claim expenses. General method: You apportion costs such as rent and utility bills based on the part of the home you use for work – you need to keep records for this.
For example, if you had 3 rooms in your home, one of which you use as an office. If your rent, energy, wifi etc bills amount to £9,000 – you can claim £3,000 as an allowable expense. (£9,000 divided by 3 rooms) Or simplified expenses:
You take a flat rate determined by HMRC, based on how many hours you work from home each month. For example, 60 hours worked at home for one month is an £18 deduction.
Expenses: Driving a car
You can claim back if you drive for business – either based on miles travelled or by apportioning car running costs. Mileage is easier – if you have a travel log of all the miles travelled for the business you can track what you can claim. 45p per mile for the first 10,000 miles then 25p per mile above 10,000 miles.
So 1,000 miles = £450 tax deduction. Car running costs – you can take care of costs such as insurance, fuel, servicing, and MOT and apportion this based on how much the car is used for business. £1,000 car running costs and car used 50% for business: £500 tax deduction.
Records for car costs are needed if questioned by HMRC.
Expenses: Buying a car
You can offset part of the car purchase costs against your income, you will receive a deduction based on the portion of business use.
The tax relief is provided as a capital allowance and depends on the CO2 emissions of the car. E.g. up to 50g/km – you get 100% of the car cost in the first year. 51g/km to 110g/km – 18% capital allowance each year till the car is sold 111g/km+ – 8% capital allowance each year till the car is sold
For example, car cost: £15,000 – CO2 emissions 100g/km + business use: 75%. £2,025 can be deducted every year until the car is sold, or the full £15,000 cost has been used up.
When selling the car, a balancing adjustment is made based on the deductions previously made, and the value of the car.
Optional: if you lease a car, this is treated as a standard expense (and not a capital allowance) – so for example Lease: £400 per month Business use: 75% Expense for a tax return: £300
If you take a trip or make a purchase that combines business and pleasure, you can only claim tax relief on costs that you can show are separate from the private part of your journey or purchase.
If you can’t split up the costs, you can’t claim tax relief on any part. So bear that in mind when you are making purchases.
Need to know
I know this all sounds super complicated, but some of these might not apply to you (you don’t travel/need a car/work from home) so just take what you need and go from there.
The good news is there are people and small businesses out there to help you and are the experts!
For me, Taxduk handles this to make it easier but also tax-efficient!
Filing a self-employment tax return
What do you need e.g UTR You need to have registered with HMRC and obtained a UTR (Unique Taxpayer Reference) to file a personal tax return.
The deadline is 5th October, but don’t worry if you missed it, you can still register. You need to have details about your earnings and expenses.
Check my previous self-employed tax guides on the different expenses & important dates.
Self Employment Tax Guide
Intro Questions
Now introducing Taxd, I used this to fill my Self Assessment, I found it such a simple process to go through. I normally dread this part, but it took about 30 minutes on my phone.
They asked me introduction questions to build a personalised set of questions
It’s almost like having a conversation with an accountant, without any tax jargon! Bonus!
Self-Employment Tax Guide Questions
The main part of the tax return includes questions about your self-employment. your earnings and expenses. I was asked about my industry & Taxd suggested the relevant expenses I can claim so that I am tax efficient.
I loved the fact you can pick a content creator or a freelancer! If you’ve got the relevant earnings and expense info, it’s so easy and quick to do which I was really happy with.
Submitting to HMRC
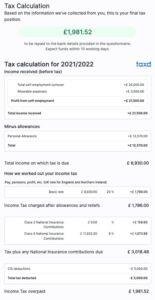
Once you have finished with all the relevant questions, you are ready to submit to HMRC within minutes. You just need to pay and review the tax return – this will be discounted using my code!
You can also book a meeting with a Taxd accountant for that additional comfort before submitting it to HMRC which is what I did. It was really helpful and informal and just takes a weight off your mind knowing you are doing everything correctly.
If you want to use Taxd for your self-assessment I have a link in my bio you can use. My code ‘helpsavemoney‘ will be auto-applied for 20% off – that’s £72 for a tax return this month! Bargain!
What I like about it is that I feel it’s done correctly with experts without feeling like I may have done something wrong and not having the guidance there.
You can also file for free with HMRC, but it’s more complex and you may want the Taxd accountant support too.
My referral code is ‘helpsavemoney‘
This guide was made with tax support from taxduk
Read more on Self-employment here

